
The tangent of the sum of the angles is equal to a fraction whose numerator is the sum of the tangent of the first and tangent of the second angle, and the denominator is one minus the product of the tangent of the first angle by the tangent of the second angle.

The tangent and cotangent sum of the alpha and beta angles can be transformed according to the following rules for converting trigonometric functions:
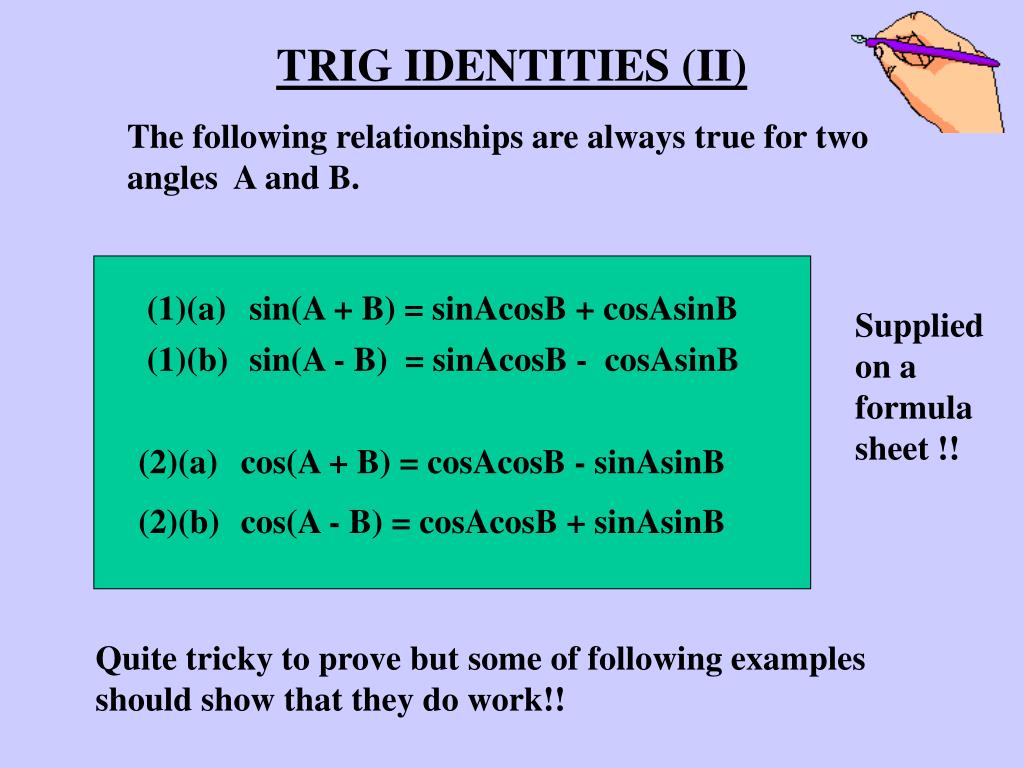
The value of the argument of the trigonometric function α / 2 is reduced to the value of the argument of the trigonometric function α. The formulas for trigonometric transformation of the half-value of the angle to its integral value are shown below. Trigonometric identities of the half-angle transformation After this, the equation with a half-angle tangent is much easier to solve. Their value lies in the fact that the trigonometric expression with their help reduces to the expression of the half-angle tangent, regardless of which trigonometric functions (sin cos tg ctg) were in the expression initially. These formulas are called the formulas of the universal trigonometric substitution. The following transformation formulas can be useful when you need to split the argument of the trigonometric function (sin α, cos α, tg α) into two and bring the expression to half the angle. Universal Trigonometric Substitution Formulas The cotangent of the double angle is equal to a fraction whose numerator is the square of the cotangent of a single angle minus one, and the denominator is twice the cotangent of the single angle The tangent of a double angle is equal to a fraction whose numerator is the double tangent of a single angle, and the denominator is equal to one minus the tangent of the square of a single angle. The cosine of the double angle is one minus the double sine square of the single angle The cosine of the double angle is equal to twice the square of the cosine of the single angle minus one The cosine of the double angle is equal to the difference of the square of the cosine of the single angle and the square of the sine of this angle The sine of the double angle is equal to twice the product of the sine by the cosine of the single angle The transformation of the double angle (the sine of the double angle, the cosine of the double angle and the tangent of the double angle) into the single angle occurs according to the following rules: If it is necessary to divide the angle in half, or vice versa, go from a double angle to a single angle, we can use the following trigonometric identities: Tangent minus alpha is equal to minus tangent alpha.įormulas for the reduction of the double angle (sine, cosine, tangent and cotangent of the double angle) The cosine of "minus alpha" will give the same value as the cosine of the alpha angle. The sine of the negative angle is equal to the negative value of the sine of the same positive angle (minus the sine alpha). In order to get rid of the negative value of the degree angle measure in calculating the sine, cosine or tangent, we can use the following trigonometric transformations (identities), based on the principles of parity or odd trigonometric functions.Īs you can see, the cosine and secant is an even function, the sine, tangent and cotangent are odd functions. Transformation of the negative angles of trigonometric functions (parity and oddness) The product of the tangent per cotangent of the same angle is one (Formula 7).
Trigonometric identities formulas sheet plus#
The unit plus the cotangent of the angle is equal to the quotient of the unit divided by the sine square of this angle (Formula 6) The sum of the unit and the tangent of the angle is equal to the ratio of one to the square of the cosine of this angle (Formula 5) see also the proof of the sum of the squares of the cosine and the sine. The sum of the squares of the sine and cosine of the same angle is one (Formula 4).

The angle of the angle is equal to one divided by the cosine of the same angle (Formula 3) The quotient of the cosine of the angle α to the sine of the same angle is equal to the cotangent of the same angle (Formula 2) See also the proof of the correctness of the transformation of the simplest trigonometric identities. The quotient of the sine of the alpha angle by the cosine of the same angle is equal to the tangent of this angle (Formula 1). To solve some problems, the table of trigonometric identities will be useful, which will make it much easier to perform the transformation of functions:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
